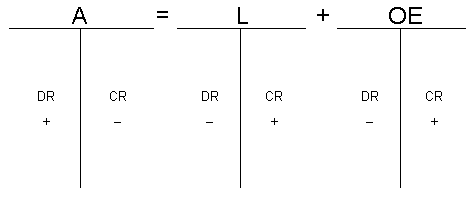Home Home
Lesson 1
Lesson 2
Lesson 3
Lesson 4
|
Basic Business Accounting
Lesson 2
Account= an individual record or form used to record and summarize information related to each asset, each liability, and each aspect of owner’s equity.
Common Accounts
Asset (A) = CASH, Account Receivables, Office Supplies, Office Equipment, Truck etc.
Liabilities (L) = Account Payables (buying merchandise on credit- short term), Note Payables (Mortgage- long term).
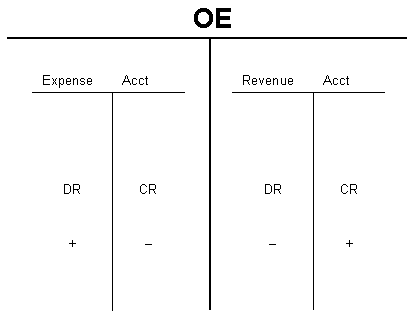
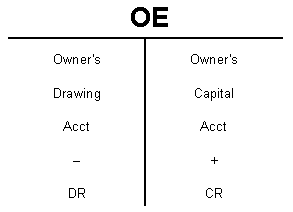
Owner’s Equity (OE) = Capital, Drawing, Revenue, Expense.
4 ways to change the OE:
- cash in- Putting personal money into the business- Capital
- cash out- Taking money out of the business for personal use- Drawing
- Revenue
- Expense- Rent Expense, Salary Expense.
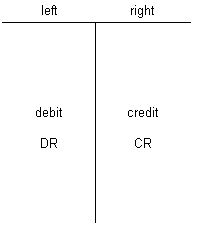
T account:
Rule in Accounting:
Debit is on the left side of the column.
Credits are on the right side.
 |
Another rule:
A is on the left side of the equation, so the increase of A is recorded in the debit (left) column.
L & OE is on the right side of the equation, so the increase of L & OE is recorded in the credit (right) column.
left right
A = L + OE
To help remember this, think about it this way: Accounts usually increase in money. That’s why A which is on the left side of the equation, the increase is on the left side. L & OE is on the right side, so the increase is on the right.
Another thing to remember is that when you owe money, your liabilities increase.
|
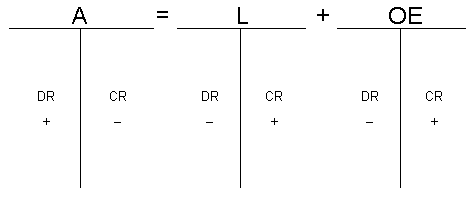
As we said before, in A, L & OE there can be many accounts.
There are 3 steps when recording a transaction:
- Which account is affected?
- Did the account go up or down?
- Is it a debit or a credit?
|